Understanding Prostate Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Prostate cancer is a prevalent condition that affects millions of men worldwide. Prostate cancer develops in the prostate gland, a small walnut-shaped organ that produces seminal fluid. The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, and it is crucial for individuals, especially men over 50, to be aware of its symptoms and risk factors.
Symptoms and Early Detection
Early detection of prostate cancer is crucial for effective treatment and improved prognosis. Recognizing the symptoms associated with this condition can significantly impact the outcome. Here are some common symptoms to be aware of:
Urinary Changes
Pay attention to difficulty initiating urination, a weak urine stream, or experiencing frequent urination. These changes may indicate an issue with the prostate.
Blood in Urine or Semen
The presence of unexplained blood in urine or semen should never be ignored. This symptom can be an early warning sign of prostate cancer or another underlying issue.
Pelvic Discomfort
Persistent pain or discomfort in the pelvic area may be indicative of prostate problems. It's essential to address any ongoing discomfort and discuss it with a healthcare professional.
Regular screenings, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test, play a vital role in early detection. These screenings help identify prostate cancer at its early stages, allowing for timely intervention and enhancing the chances of successful treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms or fall into high-risk categories, it is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate screening and guidance.
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors: What You Need to Know
Understanding the factors linked to prostate cancer is essential for taking charge of your well-being. While some factors are beyond your control, being aware empowers you to make informed choices.
Age
The risk of prostate cancer increases with age, especially in men over 50. Regular screenings become more critical as you grow older.
Family History
If a close relative has had prostate cancer, your risk goes up. Genetic factors play a role in some cases, emphasizing the importance of knowing your family history.
Geography
The prevalence of prostate cancer varies by region. Men in specific areas may face a higher risk, suggesting potential environmental or lifestyle factors.
Dietary Choices
Diets high in red meat and fatty dairy products may increase the risk. On the flip side, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins may offer protective benefits.
Lifestyle Habits
Certain choices impact prostate health. Smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of physical activity can elevate the risk.
Inflammation of the Prostate
Chronic inflammation, often due to infections or other conditions, may increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Occupational Exposures
Certain jobs with exposure to chemicals or heavy metals may contribute to an increased risk.
Obesity
Being overweight is linked to a higher risk of aggressive prostate cancer. Maintaining a healthy weight through regular exercise and a balanced diet is advisable.
Being aware of these risk factors puts you in control. Regular screenings, especially if you fall into high-risk categories, play a crucial role in early detection and managing prostate health. If you have concerns or fit into high-risk groups, consulting with a healthcare professional is essential for personalized guidance and appropriate screening measures.
Diagnostic Procedures for Prostate Cancer
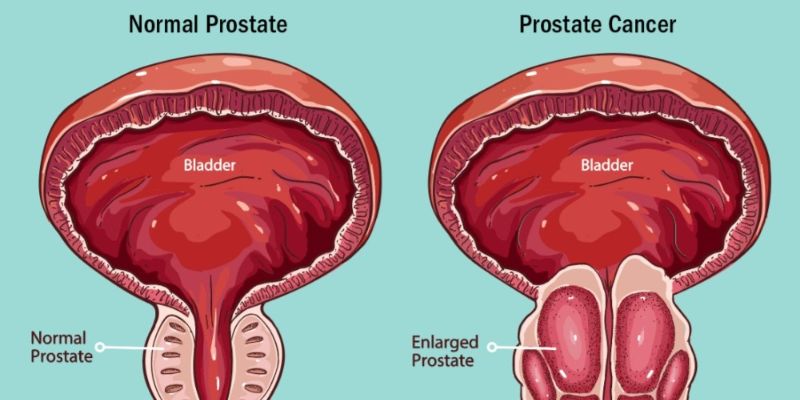
Diagnosing and treating prostate cancer requires a careful and tailored approach, considering individual health factors and the stage of the disease. Here's a concise overview of the diagnostic and treatment modalities involved.
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
This blood test measures PSA levels, a protein produced by the prostate. Elevated levels may indicate the presence of cancer, prompting further investigation.
Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
A physical examination is where a healthcare professional checks for abnormalities in the prostate by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum.
Biopsy
If abnormalities are detected, a biopsy is performed to collect tissue samples for analysis. This definitive test confirms the presence of cancer and helps determine its aggressiveness.
Imaging Tests
Advanced imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, provide detailed images of the prostate and surrounding areas, aiding in staging the cancer.
Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer
The various treatment options for prostate cancer are listed below.
Active Surveillance
For slow-growing or early-stage cancers, active surveillance involves close monitoring without immediate intervention. Regular check-ups ensure timely action if needed.
Surgery
Prostatectomy involves the surgical removal of the prostate gland. This is a common treatment for localized cancers.
Radiation Therapy
High-dose radiation is targeted at the prostate to eliminate cancer cells. This may be used as a primary treatment or after surgery.
Hormone Therapy
Suppressing the production of hormones like testosterone, which fuels the growth of prostate cancer cells. This is often used in advanced cases.
Chemotherapy
In cases where cancer has spread beyond the prostate, chemotherapy drugs may be employed to destroy or control cancer cells.
Immunotherapy
This emerging treatment stimulates the body's immune system to target and attack cancer cells.
The choice of treatment depends on factors like the cancer stage, overall health, and patient preferences. Shared decision-making with healthcare professionals ensures an individualized approach.
In conclusion, the timely and accurate diagnosis of prostate cancer, coupled with a personalized treatment plan, is crucial for effective management. Advances in medical technology and a collaborative approach between patients and healthcare providers contribute to improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life. Regular follow-ups post-treatment aid in monitoring and maintaining prostate health. If you suspect any symptoms or fall into high-risk categories, seeking medical advice promptly is essential. Understanding prostate cancer is the first step toward effective prevention, early detection, and successful treatment. By staying informed about risk factors, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps toward maintaining their prostate health.





